
IACG CAMPAIGN IV
"Solar Sources of Heliospheric Structure Observed Out of the Ecliptic"
Welcome to the homepage for the IACG Campaign IV. This service is meant to act as a meeting place for the international solar physics and space physics communities that are engaged in Campaign IV activities. This page is currently under development, evolving as the campaign itself evolves.
In this homepage you will eventually find
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- What is an IACG Campaign ?
- A description of the Goals of IACG Campaign IV
- Campaign IV News
- Information on Campaign Event Selection
-
Meetings Calendar
(last
 19Feb96)
19Feb96)
- Campaign IV-related publications Meeting Abstracts
-
Links to Mission Descriptions (last
 23Feb96)
23Feb96)
- Links to individual Investigations' Homepages
- Current Space Weather : Recent Solar, Solar-Terrestrial, Interplanetary Data and Images
- Information on Data Access
- General information and tutorials on Solar Physics and Space Physics
- Campaign IV WEB REVIEWS are here! Your participation wanted!
- References
THE IACG AND ASSOCIATED CAMPAIGNS (ref. 1,2,3)
In 1981 the space agencies of Europe, the former USSR and Eastern European countries, Japan, and the United States of America formed the Inter-Agency Consultative Group for Space Science (IACG) to provide a framework for enhancing scientific cooperation among their respective agencies: the European Space Agency (ESA), Space Research Institute (IKI), the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The IACG mission coordination is primarily achieved through conducting specific campaigns, each of which has a definitive scientific focus. There are currently four IACG campaigns in the planning or implementation stage:
- IACG Campaign I: Magnetotail Energy Flow and Non-Linear Dynamics
- IACG Campaign II: Boundaries in Collisionless Plasmas
- IACG Campaign III: Solar Events and Their Manifestations in Geospace
- IACG Campaign IV: Solar Sources of Heliospheric Structure Observed Out of the Ecliptic
A "Campaign" involves the coordinated collection, analysis, interpretation, and eventual publication of core and ancillary data sets from multi-spacecraft and ground based observations covering limited time periods to achieve specific scientific objectives. Aspects of a campaign include: determination of campaign objectives, identification of key observing time periods, identification and coordination of required data sets, and coordination of data analysis.
- For further information on the IACG:
- IACG Homepage
- IACG Contact Information
- IACG Terms of Reference
IACG CAMPAIGN IV OVERVIEW
The purpose of IACG Campaign IV Solar Sources of Heliospheric Structure Observed Out of the Ecliptic is to plan the international coordination of solar and heliospheric observations during mid-1994 through 1996 covering the ESA/NASA Ulysses spacecraft's pass over the southern polar region of the sun, the perihelion pass across the solar equator, the northern polar pass, and the northern hemisphere descent. This extensive collaborative work potentially involves solar observations by the Yohkoh spacecraft, Ground-Based Observatories, the SOHO and Coronas spacecraft, and the Spartan Space Shuttle missions, and in-situ. observations by the Ulysses, IMP-8, SAMPEX, Voyagers, Pioneers, Wind, and ICE spacecraft. A coordinated effort with theoreticians and modelers is also required for the successful completion of the campaign objectives.IACG CAMPAIGN IV OBJECTIVES (ref. 3)
At the First IACG Solar-Heliospheric Workshop on "Solar Sources of Heliospheric Structure Observed Out of the Ecliptic" (Easton, MD, January 1994), four major science topics were identified:
- Large Scale Heliosphere and Its Dependence on Solar Photospheric and Coronal Phenomena
- Topology of Coronal Streamers
- Three-Dimensional Shape of Coronal Hole Boundaries
- Solar Wind Source and Acceleration
Within these major topics, several subtopics emerged, such as
- The structure of the heliospheric magnetic field as a function of heliolatitude, and its relation to coronal structure
- The determination of the strength and structure of the photospheric magnetic field in the polar regions of the sun
- The structure, dynamics, and heliolatitude extent of transient phenomena, such as Coronal Mass Ejections from the sun and their manifestations in interplanetary space
- The dependence of the solar wind and its properties on the topology and dynamics of polar coronal holes
- Tests of solar wind acceleration models and their dependence on solar coronal field geometries
- The heliolatitude dependence of the properties of the solar wind, in particular its relationship to open and closed coronal structures, and the origin of the slow solar wind
- North-South asymmetries of the Sun at solar minimum, and a search for the axes of symmetry of the two hemispheres of the Sun
- The extent and structure of the heliospheric current sheet and its relationship with the solar magnetic neutral lime, as well as its relationship with the heliospheric extension of the coronal streamer belt
IACG CAMPAIGN IV KEY OBSERVING TIMES AND SUGGESTED OBSERVATIONAL DATA SETS
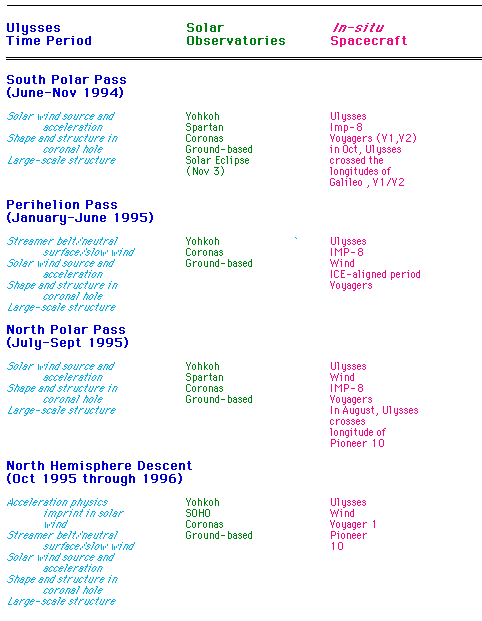
summary table of proposed key observing time periods.
CURRENT SPACE WEATHER REPORTS
- Rice University's compilation of space weather resources
Recent Solar Reports:
- NASA's Solar Data Analysis Center (SDAC) Current Solar Images of
-
Yohkoh Soft X-ray Telescope (Hiraiso Solar Terrestrial Research Center/ CRL, Japan)
- Photospheric Magnetograms (U.S. National Observatory at Kitt Peak, AZ)
- He I 10830 Å spectroheliograms (U.S. National Observatory at Kitt Peak, AZ)
- Ca II K spectroheliograms (U.S. National Solar Observatory at Sacramento Peak, NM)
- White-light coronameter images (HAO, Mauna Loa Solar Observatory, HI)
- Photospheric Magnetograms (U.S. National Observatory at Kitt Peak, AZ)
- NOAA's Space Environment Laboratory (SEL) Current Solar Images, including:
- Full Disk Magnetograms and He I 10830 Å (Kitt Peak, AZ)
- Full Disk and Region Images (Learmonth, Australia)
- Full Disk and Region Images (Holloman AFB, NM)
- Full Disk H-alpha (SEL, Boulder, CO)
- Full Disk and Region Images (Learmonth, Australia)
- SOHO science planning daily solar images, including:
- Big Bear Solar Obs., H Alpha
- Big Bear Solar Obs., White light
- Nat. Solar Obs. at Kitt Peak, He I 10830 Å
- Nat. Solar Obs. at Kitt Peak, Magnetogram, synoptic map
- Learmonth Obs., H Alpha
- Nobeyama Solar Radio Obs., Radio
- Yohkoh Soft-X Telescope, Soft X rays
- Big Bear Solar Obs., White light
- The National Solar Observatory (NSO/Kitt Peak)
-
Most Recent synoptic daily Magnetogram and Spectroheliogram images of the sun.
- Seven most recent daily magnetograms
- Seven most recent daily He I 10830 Å spectroheliograms
- Seven most recent daily magnetograms
- Current solar images from the Catania Astrophysical Observatory - Italy:
-
Chromospheric H-alpha
- Photospheric
- Current solar images from MLSO (the Mauna Loa Solar Observatory Analysis Center at the High Altitude Observatory in Boulder, Colorado ):
- Calibrated H-alpha disk and limb composite images,
- collected with the digital prominence monitor (dpm).
- Calibrated Coronal images, collected with the Mark 3 K-coronameter (mk3).
- Raw mk3, dpm limb, and dpm disk data are also available.
- Recent Solar Images from Mees Solar Observatory:
- White Light Telescope image (550K)
- Ca+K-Line Image (81K)
- Stokes Polarimeter Magnetogram (ps file)
- Stokes Polarimeter Continuum Image (ps file)
- Ca+K-Line Image (81K)
- Online data from the Hiraiso Solar Terrestrial Research Center , Japan, including
- Current Solar Radio Spectra from the Hiraiso Radio Spectrograph (HiRAS)
- Data from Australia's IPS Radio and Space Science Services, including
-
Most Recent PRESTO
solar radiospectrograph data (Culgoora Solar Observatory)
The Penticton 10cm Solar Radio Noise flux (Solar Radio Group, National Research Council Canada, Dominion Radio Astrophysical Observatory )- The latest 10cm flux daily bulletin.
- The latest 10cm flux monthly report.
Recent Solar-Terrestrial and Near-Earth Reports:
- Solar-Terrestrial Space Weather Report (NOAA Space Environment Laboratory), including
- H-alpha solar image from Holloman AFB, NM
- Geomagnetic Activity Forecast
- X-Ray Flux from GOES-7 and GOES-8
- Satellite Environment Plot (combines satellite and ground data)
- Geomagnetic Activity Forecast
- Today's magnetograms from Kiruna, Sweden (Swedish Institute of Space Physics)
-
Recent Geotail
Earth Orbit In-Situ Data
EPIC Observations - Description of Summary Data
- Data Plots for 1995
- Data Plots for 1994
- Data Plots for 1995
- CPI Observations
- Solar Wind analyzer - Monthly Intervals (Oct '92 - recent)
- Solar Wind analyzer - 5 Day Intervals (starting Feb '95)
- Hot Plasma analyzer - 5 Day Intervals (1992 - recent)
- Geotail Orbit Plots
- Solar Wind analyzer - 5 Day Intervals (starting Feb '95)
Recent Interplanetary Reports:
- Current Ulysses Observations
-
Radio data
dynamic spectra plots from URAP
- Solar wind composition data from SWICS: plots or text
- Recent Voyager Observations
- VOYAGER 2 Solar Wind Plasma plots from the MIT Plasma Science Group
- Hourly solar wind speed averages over the last 100 days
- Hourly solar wind speed averages over the last 400 days
- Recent interplanetary events identified by plasma experiment
- Solar wind dynamic pressure over the last two years
- Solar wind dynamic pressure over the entire mission
- Mission Overview Plot of Solar Wind Parameters (1977 - recent)
- Hourly solar wind speed averages over the last 400 days
DATA ARCHIVE ACCESS
This section under construction.
PUBLIC ACCESS DATA ARCHIVES:
- Coordinated Heliospheric Observations data base (COHO) Provides public access to selected parameters of heliospheric interest from Helios 1/2, ICE, Pioneer 10/11, Pioneer Venus Orbiter, Ulysses, Voyager 1/2
- Links to Solar Archives are available through the Solar Data Analysis Center (SDAC):
-
Yohkoh
- Eclipses
- SOHO
- BATSE Solar Flare Catalog
- HRTS UV Solar Atlas
- Eclipses
- NSSDC OMNIWeb - 1-hour-resolution "near-Earth" solar wind magnetic field and plasma data, energetic proton fluxes (1-60 MeV), and geomagnetic and solar activity indices.
- CDAWeb - NASA/GSFC Space Physics Data Facility and NSSDC web access to ISTP Key Parameter (KP) database, with data from Geotail, Wind, Interball and ancilliary s/c and ground observations.
- Space Physics Data System - Magnetospheric On-Line Data (MOLD)
- Navigating MOLD
- Alphabetical directory of MOLD data links
- Ulysses Predicted Orbit
-
Heliocentric Coordinates
- Daily values: 1990 - 1999
- Trajectory file available at nssdca::anon_dir:[coho.ulytrj]ulytrj.dat
- For FTP access, click here.
- Daily values: 1990 - 1999
- SAMPEX Particle Fluxes
-
Interplanetary Energetic Particle Fluxes (electron, H, He, C, N, and O)
- Plots currently available: July 1992 - December 1993
REFERENCES
1 Toward a New Era of Global Solar-Terrestrial Research, The First Inter-Agency Consultative Group (IACG) Campaign: Magnetotail Energy Flow and Non-Linear Dynamics, Report of the Workshop held in Airlie House, USA, June 1-3, 1992, ed. E.C Whipple and H. Lancaster, October 1992.2 Toward a New Era of Global Solar-Terrestrial Research, Second Inter-Agency Consultative Group (IACG) Campaign: Boundaries in Collisionless Plasmas, Report of the Workshop held in Graz, Austria, April 13-15, 1993, December 1993
3 Summary Report on the IACG Workshop on "Solar Sources of Heliospheric Structure Observed out of the Ecliptic", Easton, Maryland, January 27-29, 1994
Comments/Suggestions:
This homepage is obviously still under construction.We (Hugh Hudson and Toni Galvin, the Campaign IV Leaders) want suggestions from the Ulysses, Yohkoh, Ground Based, and other interested communities, regarding the content, format, and implementation (including management and data distribution) of the campaign. We want to utilize the experience and expertise of individual members of the interplanetary, solar, and modeling/theory communities.
We would like interested parties to contact us
Toni Galvin, galvin@umdsp.umd.edu, (301-405-6208) click here
Hugh Hudson, hudson@isass1.solar.isas.ac.jp click here
Most recent update: 26 April 1995 This page has been visited times by people outside of the University of Maryland since 7/31/96. - collected with the digital prominence monitor (dpm).

